Explain How Wave Refraction Is Different From Wave Reflection
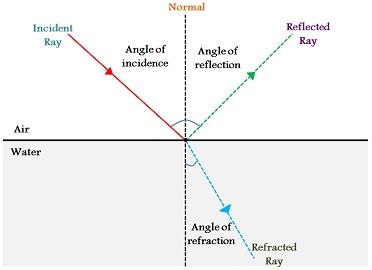
As waves approach shore they bend so wave crests are nearly parallel to the shore. Reflection is the process in which light waves falls on a surface and bounces back.
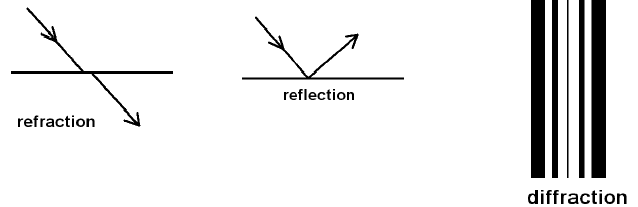
Difference Between Reflection And Refraction With Comparison Chart Key Differences
When a progressive wave traveling from a denser medium gets reflected in a rarer medium it is called Reflection at the free boundary.

. In refraction the sine of angle between the incident ray and normal maintains a constant ratio with the sine of angle of refracted ray and normal. Different materials have different densities. The reflection of a wave or a pulse can happen from two types of surfaces it can either be a fixed wall or a ring as shown in the image below.
Refraction is the bending of a wave. Using orthogonal lines illustrate how wave energy is distributed along a shoreline with headlands and bays. When a wave passes from one medium to another at any angle except 90 and 0 its line of travel changes at the interface due to the change in velocity of the wave.
In other words it is the process by which the direction of a traveling wave is changed due to the interaction with. Here the incident and the refracted waves obey Snells Law of refraction and the incident and the reflected waves obey the laws of reflection. Mar vista elementary teachers.
Refraction is the bending of waves when passes through a different medium. A headland separated by two bays. The concept should be taken into consideration whenever we analyze and read a surf report.
Reflection is the bouncing back of a wave. Reflection can simply be defined as the reflection of light when it strikes the medium on a plane. Let us know study reflection and refraction of waves by Huygens principle.
Also when the light bounces off the medium it is called a reflection. Waves such as light and sound waves can bend slow down and speed up. - Refraction is the bending of a wave.
The light entering the medium returns to the same direction. This phenomenon usually occurs in Lenses. Refraction is the turning or bending of any wave such as sound wave or light wave when it passes from one medium into another of different optical density.
That is light can pass through an object with no effect an x-ray. Reflection is the bouncing back of a wave. Waves rarely approach shore at a perfect 90 degree angle.
Refraction can be defined as the process of the shift of light when it passes through a medium leading to the bending of light. Light waves may change direction at the boundary between two transparent materials. Results may have been affected through over heating of the light box.
The wave generally changes the angle of its general direction. The mirror can reflect light. Reflection involves a change in direction of waves when they bounce off a barrier.
In reflection the angle of incidence is same as the angle of reflection. Refraction of waves involves a change in the direction of waves as they pass from one medium to another. Reflection is the property of a propagated wave being thrown back from a surface it collided with.
This is what we call refraction. How waves can be reflected absorbed or transmitted at the boundary between two different materials How to construct ray diagram to illustrate the reflection of a wave at a surface Construct ray diagrams to show refraction of a wave Use wavefront diagrams to explain refraction in terms of changes of speed Reflection of Light Mirror GCSE IGCSE Physics notes. It is assumed that the incident wave is traveling in the positive direction along the X-axis and the reflected wave is traveling in the negative direction along the x-axis.
Refraction is the change in direction of a. Refraction is the change in direction of a wave caused by the change in the waves speedExamples of waves include sound waves and light wavesRefraction is seen most often when a wave passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium. In oceanography wave refraction is the bending of a wave as it propagates over different depths.
5 Using orthogonal lines illustrate how wave energy is distributed along. The part of the wave in the deeper water moves forward faster causing the wave to bend. Wave height increases and wavelength distance between adjacent crests decreases.
Wave refraction involves waves breaking onto an irregularly shaped coastline eg. Wave speed is proportional to the depth of the water short wave different segments travel at different speeds wave energy unevenly distributed on shore orthogonal lines or wave rays drawn perpendicular to wave. In reflection the waves bounce off the surface.
As against this the angle of incidence is not similar to the angle of refraction. Reflection the bouncing off of the boundary diffraction the bending around the obstacle without crossing over the boundary transmission the crossing of the boundary into the new material or obstacle and refraction occurs along with transmission and is characterized by the. Reflection is when waves whether physical or electromagnetic bounce from a surface back toward the source.
There are essentially four possible behaviors that a wave could exhibit at a boundary. Up to 24 cash back reflection when the light wave bounced back and the the surface demonstrated refraction when the light wave bent in different surfaces. - Refraction is the bending of a wave.
A mirror reflects the image of the observer. Sometimes idyllic surf sessions depend on a concept called wave refraction. Reflection is the bouncing back of a wave.
Refraction or the bending of the path of the waves is accompanied by a change in speed and wavelength of the waves. On the contrary in refraction the waves pass through the surface that changes their speed and direction. How much do virtual assistants make per month.
Identify areas of high and low energy release. Heavy driving jobs in saudi arabia with transfer iqama. In this video I define and explain the difference between reflection refraction and.
Waves drag in the shallow water approaching a headland so the wave becomes high steep and short. Click here for glossary. Refraction is when waves whether physical or electromagnetic are deflected when the waves go through a substance.
Refraction and Reflection of Waves Using Huygens Principle As we know that when light falls on an object it bends and move through the material this is what refraction is. Although light waves provide most of the examples for refraction any other wave can also refract.

Wave Refraction Overview Examples What Is Wave Refraction Study Com

Reflection And Refraction Of Seismic Waves Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Explain How Wave Refraction Is Different From Wave Reflection"
Post a Comment